Every garden is enthralled by the majesty of lilies. They are adaptable and ideal for any house interior or garden because they are available in a number of types, colors, and sizes. Everything there is to know about lilies will be covered in this book, including their fundamental facts, characteristics, care, planting, pruning, propagation, overwintering, blooming times, and more.
Lilies – Care, Planting, Pruning
Lilies are beautiful and fragrant flowers that can be a stunning addition to any garden. Proper care, planting, and pruning are essential to ensure their health and maximize their blooming potential. Here’s a guide to help you with lily care:
1. Planting:
- Timing: Lilies are typically planted in the spring or fall, depending on the variety. Spring-planted lilies bloom in the summer, while fall-planted lilies bloom the following spring or summer.
- Location: Choose a location that receives at least six hours of sunlight a day and has well-drained soil. Lilies prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil pH.
- Soil preparation: Prepare the soil by adding organic matter like compost or well-rotted manure. This improves drainage and provides essential nutrients.
- Planting depth: Dig a hole that is two to three times the height of the bulb and place the bulb in the hole with the pointed end facing up. Space the bulbs several inches apart to allow for growth.
- Mulching: Mulch around the lilies to help retain moisture and suppress weed growth. Use organic mulch like wood chips or straw.
2. Care:
- Watering: Lilies require regular watering, especially during dry periods. Keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overhead watering, as wet foliage can promote diseases.
- Fertilizing: Apply a balanced slow-release fertilizer or a bulb fertilizer when planting. Additionally, feed the lilies with a balanced fertilizer in early spring and again after they finish blooming. Follow the package instructions for the appropriate application rate.
3. Pruning and Maintenance:
- Deadheading: Remove spent flowers by cutting them back to the stem. Deadheading prevents the formation of seeds and encourages the plant to put more energy into bulb growth rather than seed production.
- Pruning: After the lily plant has finished flowering and the foliage starts to turn yellow, you can cut back the stems to the ground. Leave the foliage intact until it has completely withered, as it provides nutrients for the bulb.
- Staking: Tall lily varieties may require staking to support the stems and prevent them from bending or breaking. Use stakes or cages and gently tie the stems to them for support.
Remember that lilies come in different varieties, so it’s important to check specific care requirements for the type of lilies you have. With proper care, lilies can provide years of beauty in your garden.
Lilies: Majestic Flowers That Captivate Every Garden
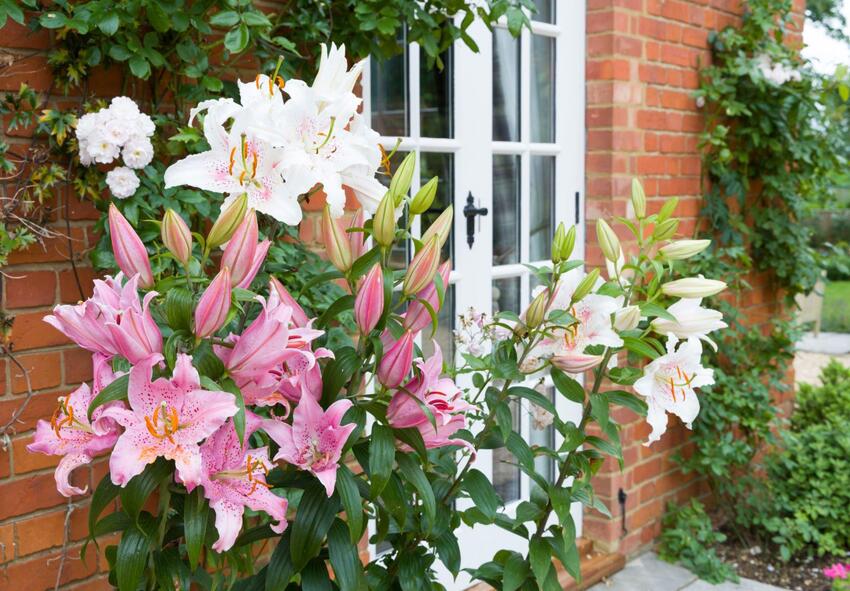

Lilies are indeed majestic flowers that captivate the beauty of any garden. With their exquisite blooms and enticing fragrance, lilies are among the most popular and cherished flowers worldwide. Here’s some information about lilies that you might find interesting:
Lilies belong to the genus Lilium and are part of the Liliaceae family. There are over 100 species of lilies, which are further divided into various hybrid varieties and cultivars. Each type has its own unique characteristics, including differences in color, shape, size, and fragrance.
Some commonly known types of lilies include Oriental lilies, Asiatic lilies, Trumpet lilies, Tiger lilies, Easter lilies, and Daylilies. Each variety possesses its own charm and appeal, with variations in flower form, petal shape, and height.
Lilies are renowned for their large, showy flowers. The blooms can range in size from a few inches to more than a foot in diameter, depending on the variety. The petals of lilies come in a wide array of colors, including shades of white, yellow, orange, pink, red, and purple. Some lilies also have captivating speckles or contrasting markings on their petals.
One of the most alluring aspects of lilies is their enchanting fragrance. Many varieties of lilies produce a sweet, lingering scent that fills the air and adds a touch of elegance to any garden or floral arrangement. The intensity of the fragrance can vary among different types of lilies.
Basic Data and Characteristics of Lilies
Lilies have large, trumpet-shaped flowers with six petals arranged in two overlapping whorls, known as tepals. The petals are usually vibrant and come in various colors, including white, yellow, pink, red, orange, and purple. Some lilies also have speckles or stripes on their petals. The size of lily flowers can vary depending on the species and cultivar. They can range from small, delicate blooms measuring a few inches across to large, impressive flowers that can be up to 10 inches or more in diameter.
Lilies have long, lance-shaped leaves that are usually arranged in whorls or spirals along the stem. The leaves can be either deciduous or evergreen, depending on the species. Lilies are herbaceous perennials, meaning they have a non-woody stem that dies back in winter and regrows from the base each year. They typically grow from bulbs or corms, which store nutrients to support their growth and flowering.
The height of lilies varies depending on the species and cultivar. They can range from dwarf varieties that grow only a few inches tall to towering types that reach several feet in height.
Different lily species and hybrids bloom at different times of the year. Some lilies flower in early spring, while others bloom in summer or even late summer to early fall. By selecting a variety of lily types, you can have continuous blooms throughout the growing season.
Table of Lily Varieties and Basic Data
| Lily Varieties | Color | Height | Blooming Time |
| White Lilies | White | 60-120 cm | July-August |
| Orange Lilies | Orange | 60-90 cm | June-July |
| Imperial Lilies | White, Pink, Purple | 90-180 cm | July-August |
| Hardy Lilies | Yellow, Pink, Red, Orange | 60-150 cm | June-July |
Lilies Types – Exploring the Differences
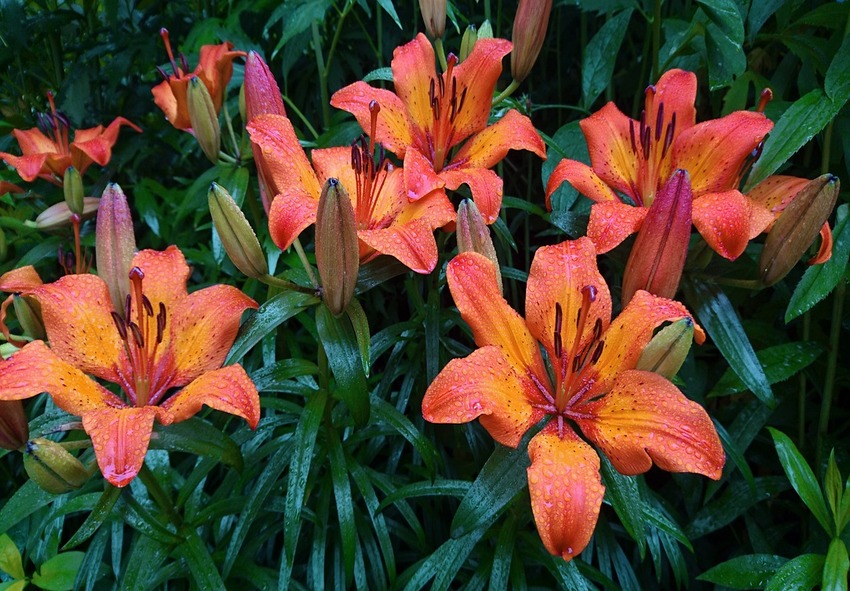

Lilies are beautiful flowering plants that belong to the genus Lilium. There are various types of lilies, each with its own unique characteristics and appearances. Here are some popular lily types and the differences between them:
- Asiatic Lilies: Asiatic lilies are known for their vibrant and bold colors. They come in a wide range of hues, including yellow, orange, red, pink, and white. Asiatic lilies have upward-facing flowers with petals that are not as trumpet-shaped as some other lily varieties. They bloom early in the summer and are typically smaller in size compared to other lilies.
- Oriental Lilies: Oriental lilies are famous for their large, fragrant flowers and elegant appearance. They usually have large, outward-facing blooms with recurved petals. Oriental lilies come in various colors, including white, pink, red, and bicolor combinations. They bloom later in the summer or early fall and are often taller than Asiatic lilies.
- Trumpet/Aurelian Lilies: Trumpet lilies, also known as Aurelian lilies, have long, trumpet-shaped flowers with a strong fragrance. They are hybrids derived from crossing Oriental and Trumpet lilies. Trumpet lilies come in shades of yellow, orange, and white, and they bloom in mid to late summer. They are generally tall and can reach heights of 5 to 6 feet.
- Tiger Lilies: Tiger lilies are easily identifiable by their distinctive speckled petals. They have large, showy blooms that are typically orange or reddish-orange with dark spots. Tiger lilies have a slightly downward-facing flower orientation and bloom in mid- to late summer. They are quite hardy and can tolerate various growing conditions.
- Daylilies: While not true lilies, daylilies are often grouped with lilies due to their similar appearance. They are known for their hardiness and ability to produce a profusion of flowers. Daylilies have trumpet-shaped blooms that come in a wide range of colors, including shades of yellow, orange, red, pink, and purple. They typically bloom for a single day but produce many buds, ensuring a continuous display throughout the summer.
These are just a few examples of lily types, and there are many other cultivars and hybrids available. Each type of lily has its own growth habits, flower shapes, colors, and blooming seasons. When selecting lilies for your garden, consider factors such as height, color preference, fragrance, and blooming time to create a visually stunning and diverse display.
Features of Lilies Care
The “Features of Lilies Care” section covers the essentials of caring for lilies, including preferred growing conditions, watering, fertilizing, and deadheading. It also provides tips for pruning to promote healthy growth and maintain their shape. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your lilies thrive and bloom for years to come.
The Essentials of Caring for Lilies
Caring for lilies involves providing the right conditions and attention to ensure their health and beauty. Here are some essential tips for caring for lilies:
Location: Lilies prefer a sunny spot with well-draining soil. They thrive in areas where they receive at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. Ensure that the soil is rich in organic matter and drains well to prevent waterlogging, which can cause bulb rot.
Planting: Lilies are usually planted in the spring or fall. Dig a hole that is two to three times deeper than the height of the bulb and space the bulbs apart according to the specific variety. Place the bulbs with the pointed ends facing upwards and cover them with soil, gently firming it around the bulbs.
Watering: Lilies require regular watering, especially during dry periods. Water the plants deeply, ensuring that the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overhead watering, as wet foliage can promote disease. Mulching around the plants can help retain moisture and suppress weed growth.
Fertilizing: Lilies benefit from regular feeding to support their growth and blooming. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer or a bulb-specific fertilizer according to the package instructions. Apply the fertilizer in early spring when new growth appears and again after the blooms have faded.
Staking: Tall lily varieties may require staking to support their stems and prevent them from bending or breaking. Place the stakes near the plants and gently tie the stems to the stakes using soft twine or plant ties. This will provide additional support as the plants grow and bloom.
Deadheading: Removing spent flowers, a process known as deadheading, helps redirect the plant’s energy into bulb development rather than seed production. Snip off the faded blooms just above the nearest healthy leaf or bud. Be careful not to damage the emerging buds or leaves.
Winter care: In colder regions, lilies may require winter protection. After the foliage has died back in the fall, cut it back to ground level. Apply a layer of mulch around the plants to insulate the bulbs and protect them from freezing temperatures. In pots or containers, you can move them to a sheltered location or provide insulation around the containers.
Pest and disease control: Lilies can be susceptible to pests such as aphids, lily beetles, and slugs. Monitor your plants regularly and take appropriate measures to control these pests, such as handpicking or using organic insecticides. Additionally, ensure good air circulation around the plants to minimize the risk of fungal diseases like botrytis or gray mold.
How to Plant Lilies
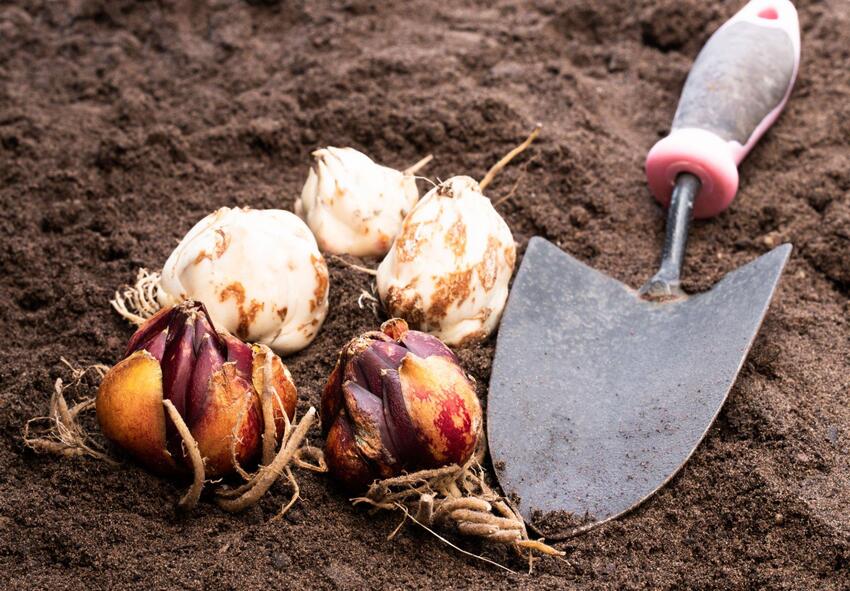

Planting lilies is a simple process that can be done in just a few steps. First, select a location that receives full sun exposure and has well-drained soil. Dig a hole that is twice the size of the bulb and place the bulb in the hole. Cover the bulb with soil and water thoroughly. Below we provide more detailed information on how to successfully plant lilies.
Step-by-Step Guide to Planting Lilies for Vibrant Blooms
Here’s a step-by-step guide to planting lilies for vibrant blooms:
Step 1: Choose the Right Lily Variety
Select the lily variety that suits your climate, soil type, and personal preferences. There are different types of lilies, such as Asiatic, Oriental, Trumpet, and Daylilies, each with its own growth requirements and blooming characteristics.
Step 2: Select an Ideal Planting Location
Lilies generally prefer well-draining soil and a location that receives at least six hours of sunlight daily. Choose a spot in your garden or flower bed that meets these requirements and provides adequate space for the lilies to grow.
Step 3: Prepare the Soil
Prepare the soil before planting. Remove any weeds, rocks, or debris from the area. Loosen the soil with a garden fork or tiller to a depth of about 12 inches. Add organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve soil fertility and drainage.
Step 4: Plant the Bulbs
Plant lily bulbs in the prepared soil during the appropriate planting season, which is typically in the fall or early spring, depending on your region and the lily variety. Dig a hole deep enough to accommodate the bulbs, usually around 6-8 inches. Place the bulbs in the hole, pointed end up, and cover them with soil, gently firming it around them.
Step 5: Water Thoroughly
After planting the bulbs, water them thoroughly to settle the soil and initiate root growth. Ensure the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged. Throughout the growing season, provide regular waterings to keep the soil consistently moist but not saturated.
Step 6: Mulch the Area
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the lilies. Mulching helps retain soil moisture, suppresses weed growth, and protects the bulbs from temperature fluctuations.
Remember to consult local gardening resources or experts for specific recommendations based on your location and lily variety, as growing conditions and care guidelines can vary.
How to Care for Lilies
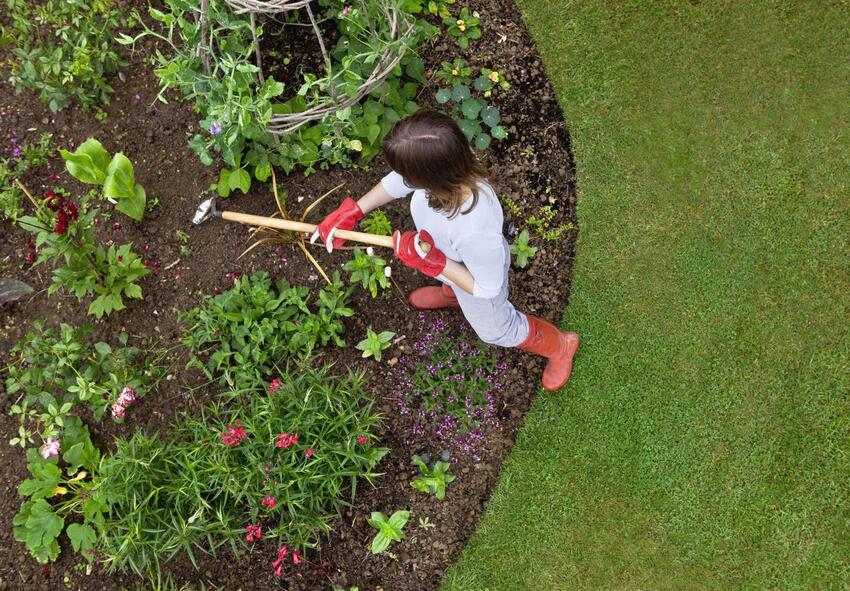

Caring for lilies is easy and requires only minimal maintenance. Lilies need to be watered regularly, especially during dry periods, and fertilizer should be applied periodically to encourage healthy growth. Deadheading faded flowers will encourage new blooms.
Caring for Lilies: From Watering to Fertilizing
Caring for lilies involves several important aspects, including watering, fertilizing, and general maintenance. Here are some guidelines to help you properly care for your lilies:
Watering:
- Lilies require consistent moisture in their soil, but they don’t like to be overly wet or waterlogged. The soil should be evenly moist, but not soggy.
- Water your lilies deeply once or twice a week, depending on the weather conditions and soil moisture. Aim to provide about 1 inch (2.5 cm) of water each week.
- Avoid overhead watering, as wet foliage can lead to diseases. Instead, water the base of the plants or use a soaker hose to keep the soil moist.
- During hot and dry periods, you may need to increase the frequency of watering to prevent the soil from drying out completely.
Soil and Drainage:
- Lilies prefer well-draining soil. If your soil is heavy or clayey, consider adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve its drainage.
- Good drainage is essential to prevent waterlogged conditions, which can cause root rot and other issues. Ensure that the planting area or container has adequate drainage holes.
Fertilizing:
- Lilies benefit from regular fertilization to support healthy growth and abundant blooms. Start fertilizing in the spring when new growth appears.
- Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer or a bulb-specific fertilizer with a formulation like 10-10-10. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates.
- Apply the fertilizer evenly around the plants, avoiding direct contact with the stems or foliage. Water the area thoroughly after fertilizing to help the nutrients reach the roots.
How to Prune Lilies
Pruning lilies is essential in maintaining their shape and promoting healthy growth. Deadheading faded flowers will encourage new blooms. It is also important to remove any damaged or diseased leaves.
Pruning Lilies: Tips for Optimal Growth and Form
The best time to prune lilies is after they have finished flowering. This is typically in late summer or early fall. Pruning at this time allows the plants to focus their energy on storing nutrients in the bulbs for the next growing season.
Start by removing the spent flowers or seed heads. This process is known as deadheading. Snip off the faded flowers just above the first set of healthy leaves. Deadheading prevents the plant from expending energy on seed production and encourages it to direct its resources towards bulb development.
Inspect the foliage of the lilies and trim any damaged, diseased, or yellowing leaves. Removing unhealthy foliage helps prevent the spread of diseases and enhances the overall appearance of the plants.
Once the foliage begins to turn yellow or brown, you can cut back the stems to a few inches above the ground. Trimming the stems helps tidy up the plant and prevents the spread of diseases and pests.
If your lilies have become too large or leggy, you can also prune them for size control. In early spring, before the new growth emerges, you can cut back the stems to a desired height. This will encourage the plant to produce more compact and sturdy growth. Before pruning your lilies, make sure to clean and sterilize your tools to avoid the transmission of diseases. Wipe the blades with rubbing alcohol or a bleach solution to disinfect them.
Collect and dispose of the pruned plant material, including flowers, leaves, and stems. Do not leave them lying around the garden as they can potentially harbor pests or diseases.
How to Propagate Lilies
Propagating lilies can be done by dividing the bulbs in the fall or spring. The new bulbs should be planted in a location that receives full sun exposure and has well-drained soil. This is a great way to expand your collection of lilies and create a stunning display in your garden.
Propagating Lilies: Techniques for Expanding Your Lily Collection
Expanding your lily collection can be an exciting and rewarding experience. There are several techniques you can use to propagate lilies and increase the number of plants in your garden. Here are some popular methods for propagating lilies:
- Bulb Division: This is the most common and easiest method of propagating lilies. Wait until late summer or early autumn when the lily bulbs have finished flowering and the foliage has died back. Carefully dig up the bulbs and separate the smaller offsets from the main bulb. Make sure each offset has roots attached. Replant the offsets at the same depth as the parent bulbs, spacing them adequately. With proper care, they will grow into mature lily plants over time.
- Scaling: Scaling is another effective technique for propagating lilies. In late winter or early spring, select healthy lily bulbs and remove the scales (modified leaves) from the bulb. Place the scales in a plastic bag with some moistened peat moss or a mixture of peat moss and perlite. Keep the bag in a warm, humid environment, such as a propagator or greenhouse, for a few weeks. During this time, bulblets will form on the scales. Once the bulblets are large enough, carefully remove them from the scales and plant them in pots or directly in the garden.
How to Overwinter Lilies
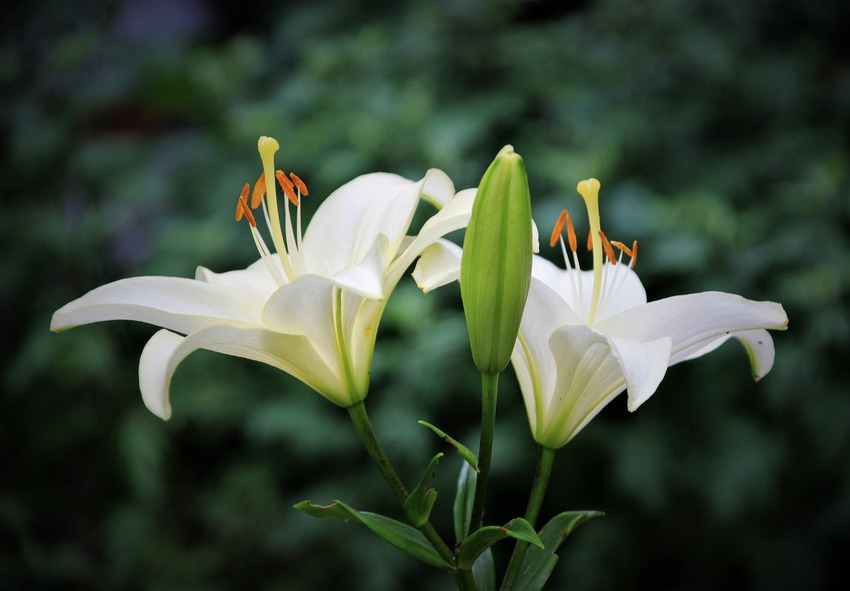

Overwintering lilies is an important step in ensuring their survival through the cold seasons. With proper preparation, you can protect the bulbs and ensure healthy growth when spring arrives.
Overwintering Lilies: Preparing Your Plants for Cold Seasons
Before the first frost sets in, you should begin preparing your lilies for winter. The exact timing will depend on your climate, but generally, it’s best to start the process in late fall or early winter. Once the foliage of your lilies starts to turn yellow and die back naturally, you can cut it back to about 2 inches above the ground. This step helps divert the plant’s energy to the bulb.
In regions with harsh winters, it’s recommended to dig up the lily bulbs and store them indoors. Use a garden fork or shovel to carefully lift the bulbs from the soil, being cautious not to damage them.
After lifting the bulbs, gently remove excess soil and debris. Inspect them for any signs of damage or disease. Allow the bulbs to dry for a few days in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area to help prevent rot during storage. Once the bulbs are dry, place them in a container with peat moss, sawdust, or vermiculite. Choose a container that allows for good air circulation and label it with the lily variety and the date. Store the container in a cool (around 40 to 50°F or 4 to 10°C), dark, and dry location, such as a basement or garage. Avoid storing them near fruits or vegetables, as they release ethylene gas that can negatively affect the bulbs.
Lily Blooming Times
Lilies bloom in the summer, and each type has its unique blooming time. For example, Asiatic lilies bloom early in the summer, while Oriental lilies bloom later in the summer. Understanding the blooming times of different lily varieties can help you plan your garden and enjoy their spectacular show for a longer period.
When Do Lilies Bloom? A Guide to the Spectacular Show
Lilies are categorized into early-, mid-, and late-season bloomers based on their flowering time. Here’s a breakdown of the bloom periods for each category:
- Early-season lilies: These lilies usually bloom in late spring to early summer, typically from May to June. Examples of early-blooming lilies include Asiatic lilies (Lilium asiaticum) and Martagon lilies (Lilium martagon).
- Mid-season lilies: These lilies bloom in the middle of summer, usually from June to July. Some popular mid-season lilies include Trumpet lilies (Lilium longiflorum), Oriental lilies (Lilium orientalis), and Turk’s cap lilies (Lilium superbum).
- Late-season lilies: These lilies bloom toward the end of summer, typically from July to August. Examples of late-blooming lilies include Tiger lilies (Lilium lancifolium) and Oriental-Trumpet lilies (Lilium ‘Conca d’Or’).
It’s important to note that these timeframes can vary depending on the specific cultivar and growing conditions. Additionally, there are some lilies that bloom in other seasons, such as the fall-blooming Surprise lily (Lycoris squamigera) or the winter-blooming Christmas lily (Lilium longiflorum).
Essential Considerations for Lilies
Lilies need to be planted in the suitable soil and position, using the necessary tools and materials, and they need to be fertilized occasionally during the growing season. A position that is shielded from high winds and has good air circulation can help lilies flourish, as can amending the soil with organic matter.
What May Be Needed? Tools and Supplies for Successful Lily Cultivation
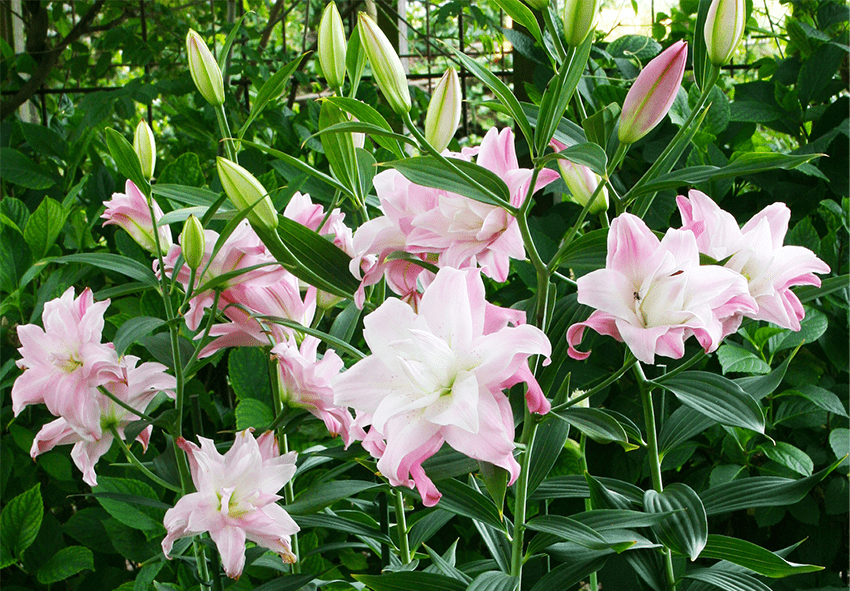
To ensure successful lily cultivation, you will need several tools and supplies. Here’s a list of essential items:
- Gardening gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, thorns, and potential skin irritations while working in the garden.
- Shovel: A sturdy shovel is necessary for digging holes and preparing the soil before planting lily bulbs.
- Trowel: A smaller hand trowel is useful for more precise digging and planting, especially when dealing with smaller bulbs or seedlings.
- Garden fork: A fork helps loosen and aerate the soil, improving drainage and providing a better environment for lily roots.
- Garden hose or watering can: Lilies require regular watering, especially during dry spells. Choose a watering method that suits your preferences and the size of your garden.
- Pruning shears: Trimming off spent flowers and removing any damaged or diseased foliage helps promote healthy growth and prevents the spread of diseases.
- Mulch: Applying a layer of organic mulch around the lilies helps retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
- Fertilizer: Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer formulated specifically for flowering plants. Apply it according to the package instructions, generally before planting and during the growing season.
- Plant markers: Labeling your lily varieties with plant markers helps you keep track of their locations, especially if you have multiple varieties or plan to divide bulbs in the future.
- Soil amendments: Depending on your soil’s composition and pH level, you may need to add organic matter or adjust the pH to create an optimal growing environment for lilies.
- Pest control measures: Monitor your lilies for common pests such as aphids, snails, slugs, or lily beetles. Depending on the severity of the infestation, you might need insecticides, organic pest controls, or physical barriers to protect your plants.
- Supports: Some lily varieties benefit from staking or other supports to prevent the stems from bending or breaking under the weight of the flowers.
- Planting containers (optional): If you prefer to grow lilies in pots or containers, make sure to choose containers with drainage holes and use a well-draining potting mix.
Remember to research the specific needs of the lily varieties you plan to cultivate, as some may have additional requirements. Providing suitable tools and supplies will help you create a nurturing environment for your lilies and increase your chances of successful cultivation.
Selecting the Right Soil for Lilies
When selecting the right soil for lilies, it’s essential to consider their specific needs. Lilies generally prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Lilies don’t like sitting in waterlogged soil, as it can lead to root rot and other problems. Ensure the soil drains well, allowing excess water to flow away easily. Avoid heavy clay soils that retain too much water.
Lilies typically thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range between 6.0 and 7.0. Conduct a soil test to determine the pH level of your soil. If it’s outside the desired range, you can amend the soil accordingly. Lilies benefit from soil that is rich in organic matter. Incorporate compost, well-rotted manure, or other organic materials into the soil before planting. Organic matter helps improve soil structure, drainage, and nutrient content.
Lilies prefer loamy or sandy soil with good structure. Loamy soil offers a balance between clay, sand, and silt, providing adequate drainage and water retention. Sandy soil allows for better drainage, while still retaining some moisture. Avoid heavy clay soils that can become compacted and hinder root growth. Lilies require a moderate level of nutrients for healthy growth and flowering. Prior to planting, you can amend the soil with a balanced slow-release fertilizer or incorporate well-decomposed compost or organic matter, which naturally enriches the soil.
It’s important to note that different lily species and hybrids may have slightly different soil preferences. Therefore, it’s beneficial to research the specific requirements of the lilies you plan to grow and adjust the soil accordingly. Additionally, consider the growing conditions in your region and any specific soil recommendations from local experts or gardening resources.
Best Places to Plant Lilies
Lilies thrive in locations that receive full sun exposure and have well-drained soil. They can be planted in gardens, containers, or raised beds. It is important to select a location that is protected from strong winds and has good air circulation.
Finding the Ideal Location for Lilies to Thrive
To find the ideal location for lilies to thrive, you need to consider several factors. Lilies generally require a significant amount of sunlight to thrive. Look for a location that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight per day. However, some lily varieties can tolerate partial shade, so make sure to choose the appropriate lily variety for the available sunlight conditions.
Lilies prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. The soil should be fertile and slightly acidic, with a pH level between 6.0 and 6.8. Conduct a soil test to determine the soil’s pH level and nutrient content. If necessary, amend the soil with compost or organic matter to improve its quality. Lilies require consistent moisture but don’t tolerate waterlogged conditions. The soil should be kept evenly moist, especially during the growing season. Ensure that the chosen location has good drainage to prevent water from pooling around the roots.
Lilies thrive in temperate climates. They typically prefer cool nights and moderate daytime temperatures. While some lilies can tolerate warmer conditions, extreme heat can stress the plants. Consider the climate of your region and choose lily varieties that are suitable for your specific climate. Strong winds can damage lilies and even break their stems. Plant your lilies in a location that offers some protection from strong winds, such as near a wall, fence, or shrubs.
Fertilizer for Lilies

Fertilizer is essential for healthy lily growth, and a slow-release fertilizer is recommended to provide a steady supply of nutrients to the plant. It should be applied periodically throughout the growing season to encourage healthy growth and vibrant blooms.
Choosing and Using Fertilizer for Healthy Lily Growth
When it comes to choosing and using fertilizer for healthy lily growth, there are a few key factors to consider. Lilies are generally heavy feeders, and providing them with the right nutrients can promote robust growth and beautiful blooms. Here are some guidelines to help you choose and use fertilizer effectively for your lilies:
- Select the right type of fertilizer: Look for a balanced, slow-release fertilizer with an NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) ratio of around 10-10-10 or 14-14-14. This balanced ratio ensures that your lilies receive equal proportions of essential nutrients.
- Timing: Apply fertilizer to lilies during their active growing season, which typically starts in early spring and continues through summer. Avoid fertilizing during dormancy or late in the growing season.
- Application method: There are two primary ways to apply fertilizer to lilies: top-dressing and liquid feeding.
- Top-dressing: Sprinkle the granular fertilizer around the base of the lily plant, being careful not to let it come into direct contact with the stems or leaves. Gently work the fertilizer into the soil surface, and then water it thoroughly.
- Liquid feeding: Dissolve the fertilizer in water according to the package instructions, and then apply it to the soil around the lilies. This method allows for faster nutrient absorption.
- Follow the instructions: Read the fertilizer packaging carefully and follow the recommended application rates. Over-fertilizing can burn the plant’s roots and cause damage, so it’s important to adhere to the instructions.
Remember, lilies have different nutritional needs depending on the variety, so it’s a good practice to research specific recommendations for the type of lily you are growing. Following these guidelines and providing your lilies with the right nutrition will help promote healthy growth and vibrant blooms.
Where to Buy Lilies
High-quality lilies can be found at our online store. We offer a wide variety of lilies in different sizes, colors, and types, making it easy to find the perfect fit for your garden or home interior.
Where to Find High-Quality Lilies: Link to the Store
Check out our online store if you’re seeking for premium lilies to enhance your landscape or give as a gift. Your needs will be met by our large collection of lilies in a range of shapes, hues, and varieties.
You can discover what you’re looking for whether you prefer the striking and brilliant colors of red, pink, or yellow lilies or the classic elegance of white lilies. From little and delicate to enormous and spectacular, we have lilies in different shapes and sizes, allowing you to pick the ideal one for your garden or a special someone.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Lilies
1. What are the different types of lilies I can grow in my garden?
Lilies come in various types, including Asiatic, Oriental, Trumpet, and Daylilies. Each type has its unique characteristics and bloom times. Asiatic lilies are early bloomers with vibrant colors, while Oriental lilies are known for their fragrant and large flowers. Trumpet lilies have trumpet-shaped blooms and can reach impressive heights. Daylilies are versatile and provide a pop of color throughout the summer.
2. When is the best time to plant Holland lilies?
The ideal time to plant lilies depends on your climate, but generally, it’s best to plant lily bulbs in the fall, about 2-4 weeks before your first frost date. This allows the bulbs to establish their roots before winter. In regions with mild winters, you can also plant them in early spring when the ground is workable.
3. How do I care for my lilies to ensure they thrive?
Lilies require well-draining soil, plenty of sunlight (at least 6 hours a day), and regular watering. Mulching can help retain moisture and suppress weeds. To encourage healthy growth, use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in the spring. Deadheading spent blooms and cutting back stems after flowering can promote more blooms and a tidy appearance.
4. Can I order lilies from your online store?
Yes, you can! Our online store offers a wide selection of lilies plants, including different varieties and colors. We take pride in providing top-quality plants that are carefully cultivated and shipped with care to ensure they reach you in perfect condition. Visit our online store to explore our collection and place your order for a delightful addition to your home or garden.
5. Are lilies safe for pets?
Many lily species, particularly Easter lilies (Lilium longiflorum) and tiger lilies (Lilium lancifolium), are toxic to cats and can cause severe kidney damage if ingested. To ensure your pets’ safety, it’s best to avoid planting these types of lilies if you have cats. Instead, consider pet-safe alternatives like daylilies (Hemerocallis spp.) or other non-toxic plants for your garden.
Published: 30.06.2023

Comments: 1
24.07.2025 at 18:10
This is an excellent guide with very detailed tips for caring for lilies. I appreciate all the helpful information and look forward to using these insights to ensure my lilies thrive.